DSA: Locking tf in - Part 3
26/12/2024
6
Min.
3 traversal for graphs + A Java graph editor for the vines
Graph
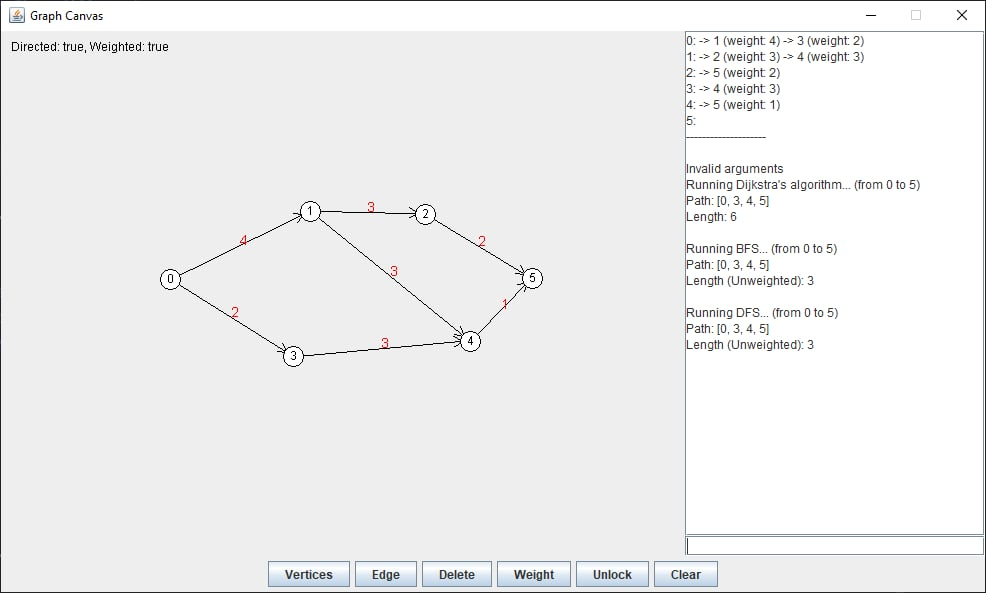
Java graph editor I made for fun: yuk068 - GraphCanvas.
Problem List (3 Problems)
G4G - Dijkstra Algorithm
ArrayList<Integer> dijkstra(ArrayList<ArrayList<iPair>> adj, int src) {
int V = adj.size();
ArrayList<Integer> dist = new ArrayList<>(Collections.nCopies(V, Integer.MAX_VALUE));
PriorityQueue<iPair> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a.second - b.second);
dist.set(src, 0);
pq.add(new iPair(src, 0));
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
iPair current = pq.poll();
int u = current.first;
int d = current.second;
if (d > dist.get(u)) continue;
for (iPair neighbor : adj.get(u)) {
int v = neighbor.first;
int weight = neighbor.second;
if (dist.get(u) + weight < dist.get(v)) {
dist.set(v, dist.get(u) + weight);
pq.add(new iPair(v, dist.get(v)));
}
}
}
return dist;
}
Initialize: Look-up table dist for distances, priority queue pq for traversal. Populate dist with \(\infty\), set src node in dist to 0 and add src to pq.
Algorithm:
- While
pqis not empty, poll a node, get its destinationuand distanced. - If
dis greater thanu’s distance in tabledistthen skip the suboptimal path. - Otherwise get all edges of
ufrom adjacency listadj, getu’s destinationsvand it’s weightweight. - If current distance to
uin tabledist+weightis less than current distance tovindistthen updatev’s distance in tabledistwith distance tou+weight. After that, addvtopqwith the newly updated distance tovindist.
G4G - BFS of Graph
public ArrayList<Integer> bfsOfGraph(int V, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj) {
ArrayList<Integer> bfs = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
queue.offer(0);
visited[0] = true;
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int node = queue.poll();
bfs.add(node);
for (Integer neighbor : adj.get(node)) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
queue.offer(neighbor);
visited[neighbor] = true;
}
}
}
return bfs;
}
// More consistent with the DFS problem below
public ArrayList<Integer> bfsOfGraph(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj) {
int V = adj.size();
ArrayList<Integer> bfs = new ArrayList<>();
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
queue.offer(0);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
int node = queue.poll();
if (!visited[node]) {
bfs.add(node);
visited[node] = true;
for (int neighbor : adj.get(node)) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
queue.offer(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
return bfs;
}
G4G - DFS of Graph
// Iterative
public ArrayList<Integer> dfsOfGraph(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj) {
int V = adj.size();
ArrayList<Integer> dfs = new ArrayList<>();
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
stack.push(0);
while (!stack.isEmpty()) {
int node = stack.pop();
if (!visited[node]) {
dfs.add(node);
visited[node] = true;
// Note: increment or decrement matter if order in output is require
// (eg. in order of original adj -> decrement)
// Kinda like choosing to go left or right in trees
for (int i = adj.get(node).size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
int neighbor = adj.get(node).get(i);
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
stack.push(neighbor);
}
}
}
}
return dfs;
}
// Recursive
public ArrayList<Integer> dfsOfGraph(ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj) {
int V = adj.size();
ArrayList<Integer> dfs = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] visited = new boolean[V];
dfsHelper(0, adj, visited, dfs);
return dfs;
}
private void dfsHelper(int node, ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer>> adj, boolean[] visited, ArrayList<Integer> dfs) {
visited[node] = true;
dfs.add(node);
for (Integer neighbor : adj.get(node)) {
if (!visited[neighbor]) {
dfsHelper(neighbor, adj, visited, dfs);
}
}
}
Minimum Spanning Tree
Kruskal’s Algorithm
class Kruskal {
static class Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
Edge(int src, int dest, int weight) {
this.src = src;
this.dest = dest;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
// Find the root of the set containing element x
static int find(int parent[], int x) {
if (parent[x] == x) return x;
return parent[x] = find(parent, parent[x]);
}
// Union by rank
static void union(int parent[], int rank[], int x, int y) {
int rootX = find(parent, x);
int rootY = find(parent, y);
if (rootX != rootY) {
if (rank[rootX] > rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
} else if (rank[rootX] < rank[rootY]) {
parent[rootX] = rootY;
} else {
parent[rootY] = rootX;
rank[rootX]++;
}
}
}
// Function to find MST using Kruskal's algorithm
public static ArrayList<Edge> kruskal(int V, ArrayList<Edge> edges) {
// Sort the edges by weight
Collections.sort(edges, Comparator.comparingInt(e -> e.weight));
int[] parent = new int[V];
int[] rank = new int[V];
// Initialize disjoint sets
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
parent[i] = i;
rank[i] = 0;
}
ArrayList<Edge> mst = new ArrayList<>();
for (Edge edge : edges) {
int x = find(parent, edge.src);
int y = find(parent, edge.dest);
if (x != y) {
mst.add(edge);
union(parent, rank, x, y);
}
}
return mst;
}
}
Prim’s Algorithm
class Prim {
static class Edge {
int src, dest, weight;
Edge(int src, int dest, int weight) {
this.src = src;
this.dest = dest;
this.weight = weight;
}
}
// Function to find MST using Prim's algorithm
public static ArrayList<Edge> prim(int V, ArrayList<ArrayList<Edge>> adj) {
// Priority queue to select the edge with the minimum weight
PriorityQueue<Edge> pq = new PriorityQueue<>(Comparator.comparingInt(e -> e.weight));
// To keep track of vertices included in the MST
boolean[] inMST = new boolean[V];
ArrayList<Edge> mst = new ArrayList<>();
// Start from vertex 0
inMST[0] = true;
// Add edges of vertex 0 to the priority queue
for (Edge edge : adj.get(0)) {
pq.add(edge);
}
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
// Get the edge with minimum weight
Edge edge = pq.poll();
int u = edge.src;
int v = edge.dest;
// If v is not included in the MST
if (!inMST[v]) {
mst.add(edge);
inMST[v] = true;
// Add all edges from v to the priority queue
for (Edge nextEdge : adj.get(v)) {
if (!inMST[nextEdge.dest]) {
pq.add(nextEdge);
}
}
}
}
return mst;
}
}
class Graph {
int vertices;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer[]>> adjacencyList; // 0: destination, 1: weight
Graph(int vertices) {
this.vertices = vertices;
adjacencyList = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < vertices; i++) {
adjacencyList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
}
// Undirected graph
void addEdge(int src, int dest, int weight) {
adjacencyList.get(src).add(new Integer[]{dest, weight});
adjacencyList.get(dest).add(new Integer[]{dest, weight});
}
}
public class PrimDriver {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Example graph with 5 vertices
Graph graph = new Graph(5);
// Adding edges (src, dest, weight)
graph.addEdge(0, 1, 2);
graph.addEdge(0, 3, 6);
graph.addEdge(1, 2, 3);
graph.addEdge(1, 3, 8);
graph.addEdge(1, 4, 5);
graph.addEdge(2, 4, 7);
graph.addEdge(3, 4, 9);
// Call Prim's algorithm implementation
List<int[]> mst = primMST(graph);
// Output the MST
System.out.println("Minimum Spanning Tree (Edge List):");
for (int[] edge : mst) {
System.out.println("(" + edge[0] + ", " + edge[1] + ") with weight " + edge[2]);
}
}
public static List<int[]> primMST(Graph graph) {
int v = graph.vertices;
ArrayList<ArrayList<Integer[]>> adj = graph.adjacencyList;
List<int[]> mst = new ArrayList<>();
PriorityQueue<Integer[]> pq = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> a[2] - b[2]); // Min-heap for edges
boolean[] visited = new boolean[v];
Arrays.fill(visited, false);
// Start from vertex 0
visited[0] = true;
for (Integer[] edge : adj.get(0)) {
pq.add(new Integer[]{0, edge[0], edge[1]}); // Add edges from vertex 0
}
while (!pq.isEmpty()) {
Integer[] edge = pq.poll(); // {source, destination, weight}
int src = edge[0];
int dest = edge[1];
int weight = edge[2];
// If the destination is already visited, skip it
if (visited[dest]) {
continue;
}
// Add the edge to the MST
mst.add(new int[]{src, dest, weight});
visited[dest] = true;
// Add all edges from the new vertex to the priority queue
for (Integer[] next : adj.get(dest)) {
if (!visited[next[0]]) {
pq.add(new Integer[]{dest, next[0], next[1]});
}
}
}
return mst;
}
}